How to Set Up a Chess Board Step-by-Step
Your Quick Guide to a Correct Chess Board Setup
How to Set Up a Chess Board the Correct Way (Image: Mashup Math via Getty)
Have you ever been confused about where to start when setting up a chess board? If so, you are not alone, as it is extremely common to forget the positions of a correct chess board setup, especially when you don’t play very often. Luckily, correctly setting up a chess board is a relatively easy task. If you can apply a few simple rules, then the entire setup process can be easy and straightforward.
In this short guide on how to set up a chess board, we will walk you through setting up your board step-by-step so that you can position all of your pieces in the correct spots on your chess board and be ready to play a game of chess in just a few minutes. This guide also includes a link to download a free PDF reference sheet that you can print out and use as a guide whenever you need it.
In addition to the written directions below, this guide also includes image diagrams that you can reference while setting up your chess board. You may want to have this guide handy while you are actually setting up your board. Are you ready to get started?
How to Set Up a Chess Board
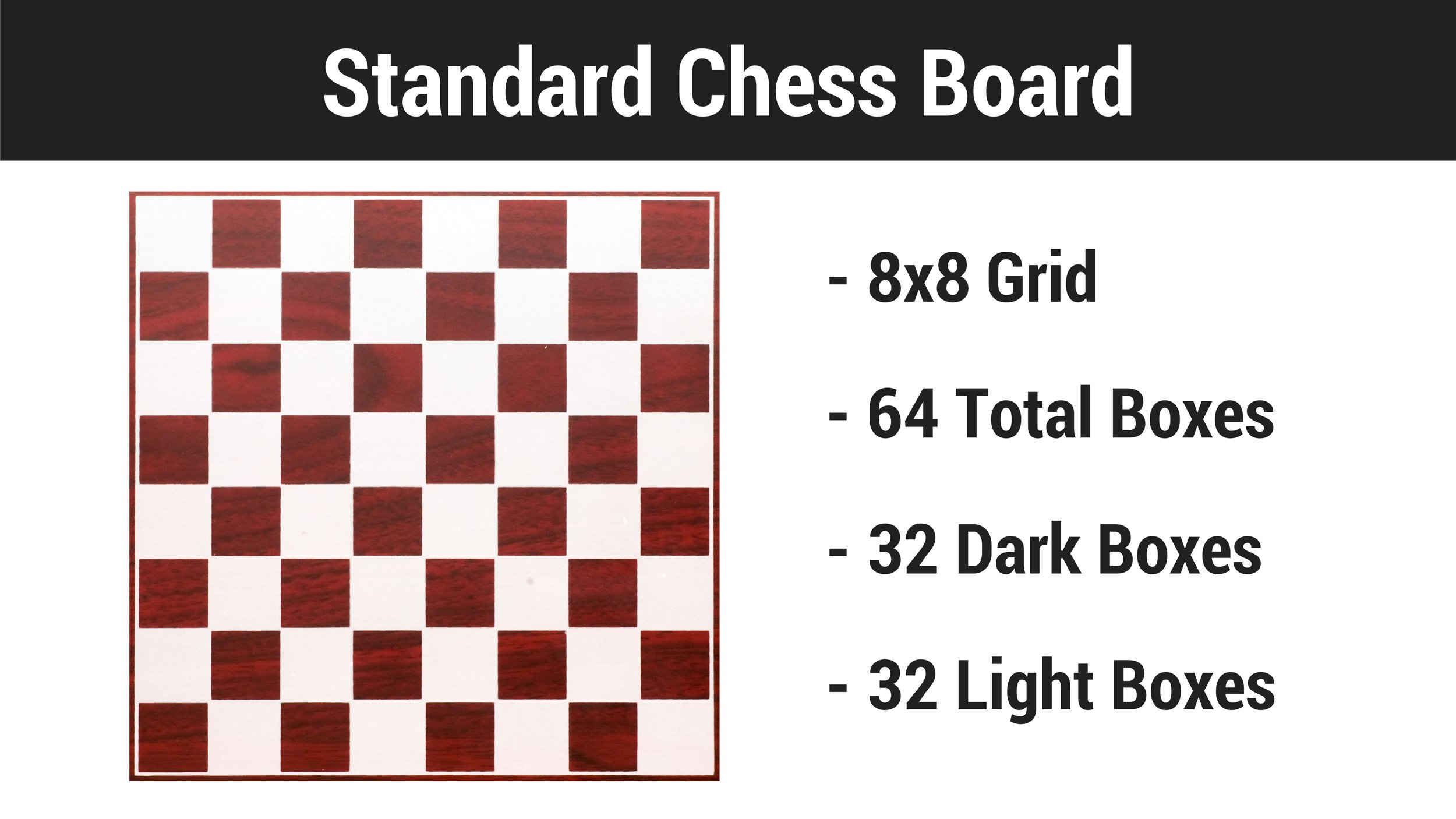
The Standard Chess Board
Before we learn how to set up the pieces on a chess board, let’s take a look at the features of an actual chessboard. The board is an 8x8 grid with 64 squares, alternating between light colors and dark colors. There are an equal amount of light squares as there are dark squares: 32 of each.
Now that you are familiar with the chess board, are you ready to learn how to correctly set up a chess board?
The first step is to make sure that the chess board is facing in the right direction. Whenever playing chess, the lower-right square must always be a light-colored square. To make sure that your board is aligned correctly, make sure that, from the player’s perspective, that the right-most square in the first-row facing you is light-colored. If it is not, then rotate your board clockwise by 90 degrees.
The diagram below shows a chess board that is correctly oriented and one that is incorrectly oriented.
Chess Board Setup Step One: The lower-right square must always be light-colored.
Chessboard Setup: The Pieces and Their Names
Once your chess board is oriented correctly, it’s time to set up the pieces.
Chess Board Setup: Know the Pieces and Their Names (Image: Mashup Math FP)
Each player starts a game of chess with 16 total pieces:
8 Pawns
2 Rooks
2 Knights
2 Bishops
1 Queen
1 King
Each piece has a specific starting spot on the chess board. All of the pieces go on the bottom two rows (the first player’s pieces) and the top two rows (the second player’s pieces).
The following instructions are the same for both the dark set of pieces and the light set of pieces. For the sake of simplicity, the diagrams below will show you how to set up both players chess pieces so that both players pieces are correctly positioned before you start playing a game.
Chess Board Setup: Player Perspective
How to Set Up a Chess Board Step #1: Position the Queens
The first step to setting up a chess board is to correctly position the Queens.
Position the Light Queen on the center-most light square and the Dark Queen is positioned directly across from her on the center-most dark square, as shown in the figure below.
It is very important that the Queens are facing each other and are on a colored square that corresponds with the color of the game pieces (i.e. the light queen goes on a light square and the dark queen goes on a dark square).
How to Set Up a Chess Board: The light queen goes on the center-most light square and the dark queen goes on the center-most dark square. The queens should be directly across from each other.
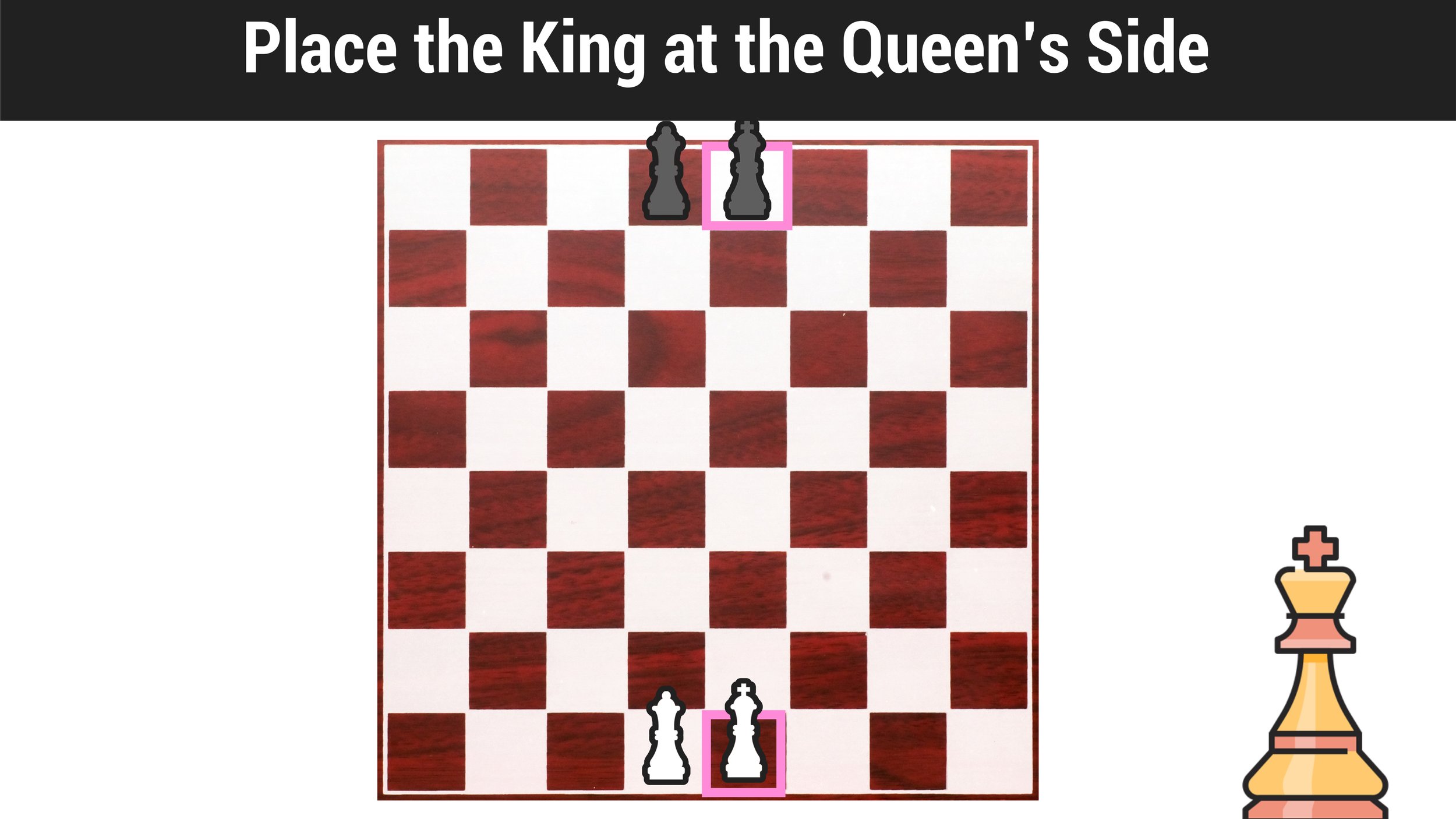
How to Set Up a Chess Board Step #2: Position the Kings
The entire process of setting up a chess board gets easier once you have correctly positioned the queens.
The next step is to place the King at the Queen’s side at the center of the board.
Chess Board Setup: The Queen will always go on the center-most square that matches her own color and the King goes on the remaining center-most square at her side.
How to Set Up a Chess Board Step #3: Complete the First Row
Now that the King and Queen are correctly positioned, the third step is to complete the first row by placing the remaining non-pawn pieces in height order (tallest to shortest) from the center of the first row outwards.
This positioning means that Bishops come first, then the Knights, and finally the Rooks. A good way to remember this positioning is: Bishops next to royalty, then Knights, and Rooks in the corners.
Bishops next to royalty, then Knights, and Rooks in the corners.
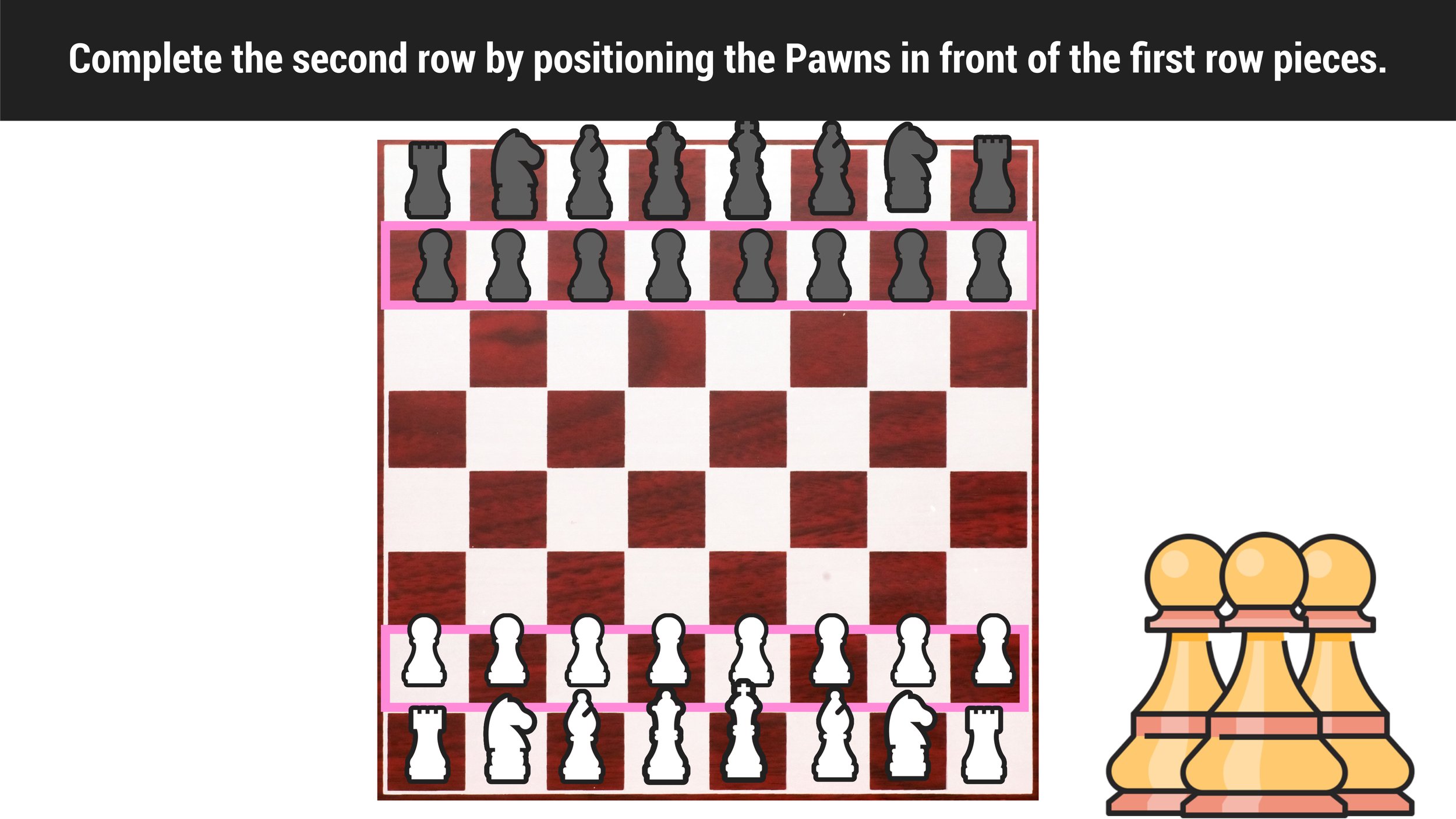
How to Set Up a Chess Board Step #4: Complete the Second Row
The fourth and final step to setting up a chess board is to complete the second row by positioning the Pawns in front of the first row pieces.
The Pawns are your smallest pieces, and lining them up across the second row is simple. Once you have completed this step, your chess board is successfully set up and you are ready to play!
How to Set Up a Chess Board: The final step to setting up a chess board is to complete the second row by positioning the Pawns in front of the first row pieces.
Chess Board Setup: Quick Reference
That’s all there is to it! We have just successfully set up a chess board with all of the pieces in their correct positions.
If you need some extra help remembering the correct chessboard setup, you can check out the tips below and download and print our free How to Set Up a Chess Board PDF Diagram, which you can keep with your chess pieces and board as a quick reference whenever you want to play.
▶ Click Here to Download Your Free Chess Board Setup Reference Diagram PDF
Click image to preview
How to Set Up a Chess Board: Quick Tips
Many chess players rely on remembering that the Queen loves fashion and always makes sure that her dress matches her square (i.e. she always stands on the color of her piece to start any game). Again, if you can remember to correctly position the Queen, then placing all of the other pieces becomes much easier.
Once you have mastered the proper chessboard setup, you are ready to start playing games! Photo by Tanner Mardis on Unsplash
You can also improve your ability to quickly and accurately set up a chess board simply by practicing the steps as often as possible. The more that you follow the steps, the quicker you will end up memorizing the proper set up of a chess board (and you will also learn how to identify when a board is set up incorrectly). So, if you have the time, go ahead and complete your chess board setup, then clear the pieces and do it again and again until you feel like an absolute pro.
Before you know it, you’ll be setting up your board and starting games in no time. So, now is the time to gather your chess pieces and your board, set up a game, find a friend to play with, and have some fun!
Keep Learning:
Is Chess a Sport?
The subject of whether or not chess is considered a sport is extremely polarizing. On one hand, many see chess as merely a game of intense strategy and intellectual skill. For others, chess is clearly a sport due to its competitive nature and high stakes competitive nature.